Write-Ahead Log (WAL)
Write-Ahead Log (WAL) records all changes before applying them to storage. This enables concurrent writes, crash recovery, and replication.
WAL is enabled by default and recommended for all tables.
Why WAL matters
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Concurrent writes | Multiple clients can write simultaneously without blocking |
| Crash recovery | Committed data is never lost — replay from log after restart |
| Replication | WAL enables high availability and disaster recovery |
| Out-of-order handling | Late-arriving data is merged efficiently |
| Deduplication | Enables DEDUP UPSERT KEYS |
In QuestDB Enterprise, WAL segments are sent to object storage immediately on commit, enabling real-time replication to standby nodes.
Creating WAL tables
WAL is enabled by default for partitioned tables:
CREATE TABLE prices (
ts TIMESTAMP,
ticker SYMBOL,
price DOUBLE
) TIMESTAMP(ts) PARTITION BY DAY;
-- This is a WAL table (default)
You can be explicit with the WAL keyword:
CREATE TABLE prices (...)
TIMESTAMP(ts) PARTITION BY DAY WAL;
Requirements
WAL tables must be partitioned. Non-partitioned tables cannot use WAL:
-- Non-partitioned = no WAL (not recommended)
CREATE TABLE static_data (key VARCHAR, value VARCHAR);
-- Partitioned = WAL enabled (recommended)
CREATE TABLE prices (...)
TIMESTAMP(ts) PARTITION BY DAY;
Always use partitioned tables to get WAL benefits.
Checking WAL status
Check if a table uses WAL:
SELECT name, walEnabled FROM tables() WHERE name = 'prices';
Check WAL table status:
SELECT * FROM wal_tables();
If WAL transactions are suspended (rare), resume them:
ALTER TABLE prices RESUME WAL;
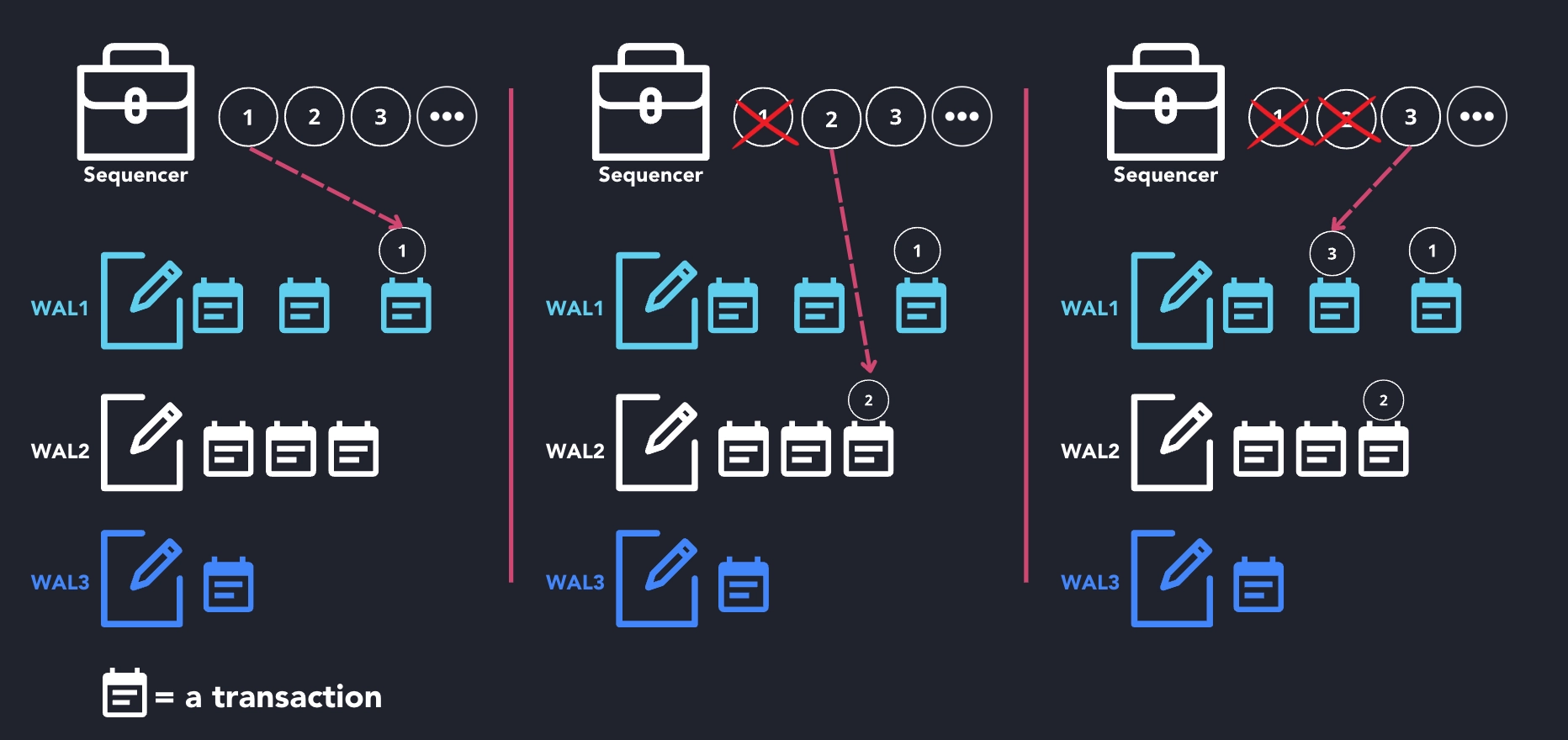
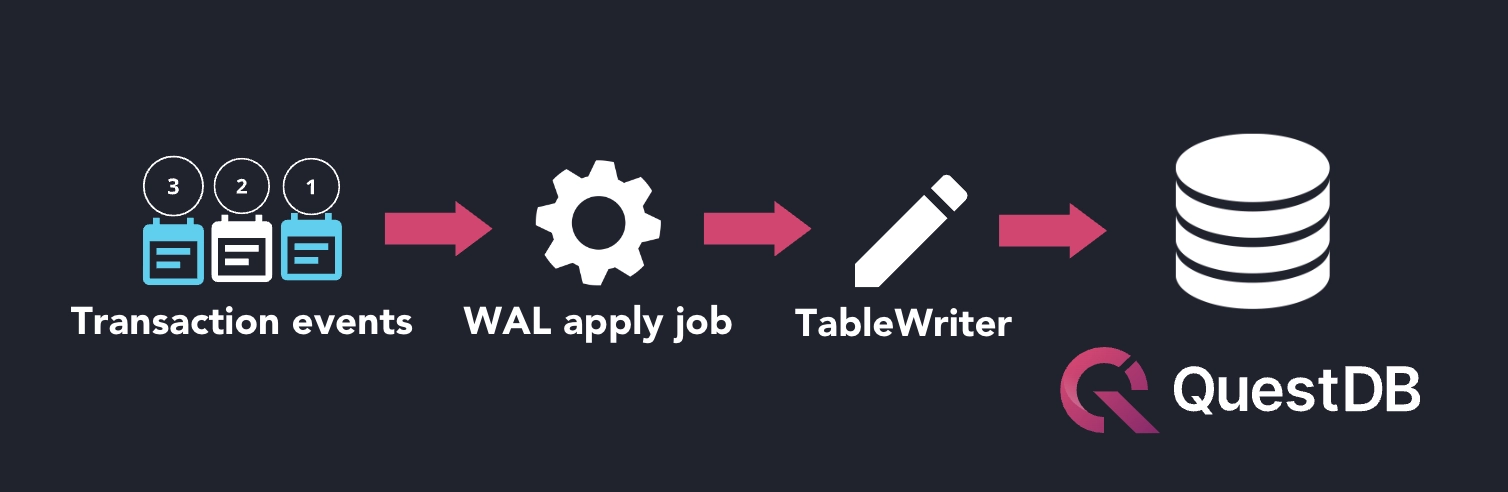
How WAL works
When data is written to a WAL table:
- Data is written to WAL segments (fast sequential writes)
- Transaction is committed and acknowledged to client
- WAL apply job merges data into table storage asynchronously
- In Enterprise, WAL segments replicate to object storage
This decouples the commit (fast) from storage application (background), enabling high write throughput.
Configuration
WAL behavior can be tuned via server configuration:
cairo.wal.enabled.default— WAL enabled by default (default:true)- Parallel threads for WAL application — see WAL configuration
To convert an existing table between WAL and non-WAL:
ALTER TABLE prices SET TYPE WAL;
-- Requires database restart to take effect
See ALTER TABLE SET TYPE for details.
See also
- Replication — high availability and failover
- Deduplication — requires WAL
- CREATE TABLE — WAL syntax